Innovation in the medical device industry is ever-evolving. Driven by the demand for highly reliable, miniaturized, and cost-effective components, metal stampings have emerged as a critical element in the development of these devices.
The Role of Metal Stampings in Medical Devices
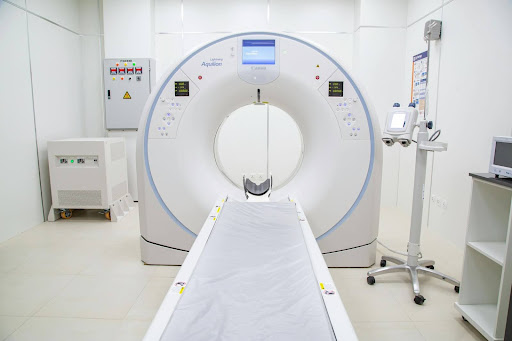 Metal stamping is a fabrication process that transforms flat metal sheets into intricate, three-dimensional components using specialized dies and presses. This efficient process guarantees high precision and consistency, qualities which are non-negotiable in the medical field. Medical stampings are found in a wide range of products, including surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment. The tight tolerances achieved during the stamping process ensure that each component meets the rigorous standards required for medical use.
Metal stamping is a fabrication process that transforms flat metal sheets into intricate, three-dimensional components using specialized dies and presses. This efficient process guarantees high precision and consistency, qualities which are non-negotiable in the medical field. Medical stampings are found in a wide range of products, including surgical instruments, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment. The tight tolerances achieved during the stamping process ensure that each component meets the rigorous standards required for medical use.
Read more »


 Every detail is critical in the production of safe and effective batteries for cell phones, vehicles, appliances, and countless other essential products. From the chemistry of the cells to the configuration of the casing, each component plays a pivotal role in the performance and longevity of the battery. One often-overlooked aspect is the choice of metals for battery stampings – the materials used to shape and support the structure of the battery. There are a number of crucial considerations involved in making the right choice.
Every detail is critical in the production of safe and effective batteries for cell phones, vehicles, appliances, and countless other essential products. From the chemistry of the cells to the configuration of the casing, each component plays a pivotal role in the performance and longevity of the battery. One often-overlooked aspect is the choice of metals for battery stampings – the materials used to shape and support the structure of the battery. There are a number of crucial considerations involved in making the right choice. In industrial applications, materials with desirable properties play a pivotal role in shaping innovation.
In industrial applications, materials with desirable properties play a pivotal role in shaping innovation. 
